Introduction
Modern brain diagnostic instruments have revolutionized how we understand, diagnose, and treat disorders of the central nervous system. From non-invasive imaging techniques to precise neurological exam equipment, today's medical technology allows doctors to detect abnormalities earlier, leading to better patient outcomes.
In Gentaur, we explore the top brain scan machines, their functions, and how they contribute to early detection of brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, stroke, and brain tumors.
Why Brain Diagnostics Matter
The human brain is incredibly complex, and diagnosing neurological disorders requires equally sophisticated technology. Traditional symptoms-based diagnosis is no longer enough. Now, clinicians rely on advanced brain imaging technologies and neurodiagnostic tools to:
Visualize brain structure and activity
Monitor cognitive decline
Detect tumors or lesions
Measure electrical signals in the brain
Guide neurosurgical procedures
These tools form the foundation of modern neurology diagnostics and support personalized treatment strategies.
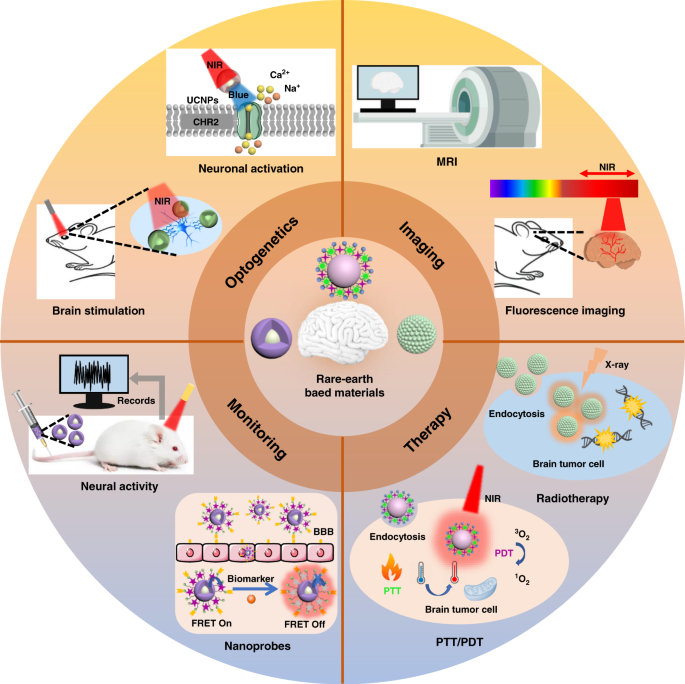
Top Brain Diagnostic Instruments Used Today
1. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
The MRI machine is one of the most powerful brain scan machines available. It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain’s anatomy.
Applications:
Detecting brain tumors
Diagnosing multiple sclerosis
Monitoring traumatic brain injury
Identifying early signs of dementia
Advantages:
Non-invasive
No radiation
High-resolution images of soft tissues
2. EEG (Electroencephalography)
The EEG test is a key diagnostic tool used to measure electrical activity in the brain via electrodes placed on the scalp. It is widely used in epilepsy diagnosis and monitoring seizure activity.
Applications:
Seizure detection
Sleep disorder analysis
Brain death confirmation
Real-time neural monitoring during surgery
Advantages:
Real-time data
Portable EEG systems available
Painless and quick
3. CT Scan (Computed Tomography)
A CT scan is often used in emergency settings due to its speed. It combines X-rays and computer processing to generate cross-sectional images of the brain.
Applications:
Stroke diagnosis
Brain hemorrhage detection
Head trauma assessment
Advantages:
Fast results
Widely available in hospitals
Ideal for acute situations
4. PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography)
PET scans are used to evaluate brain function rather than structure. This makes them ideal for detecting metabolic changes and brain activity patterns, often used in dementia research and Parkinson’s disease diagnostics.
Applications:
Alzheimer’s detection
Parkinson's disease monitoring
Brain tumor activity tracking
Advantages:
Functional insights
Can identify early changes before structural damage occurs
5. MEG (Magnetoencephalography)
MEG detects magnetic fields generated by neuronal activity. It provides highly accurate spatial and temporal brain mapping, used especially in epilepsy surgery planning.
Applications:
Pre-surgical planning
Localizing seizure foci
Studying brain networks
Advantages:
Excellent temporal resolution
Non-invasive
Safe for repeated use
6. fMRI (Functional MRI)
While traditional MRI captures brain structure, fMRI measures changes in blood oxygenation and flow that occur with neural activity. It’s commonly used in cognitive neuroscience and pre-operative brain mapping.
Applications:
Studying brain regions involved in language, memory, and emotion
Planning brain surgeries
Understanding mental health disorders
Portable and Point-of-Care Neurodiagnostic Tools
With the advancement of wearable technologies, portable EEGs and neurological exam equipment are becoming more accessible for remote and ambulatory monitoring.
Portable EEG caps enable long-term seizure monitoring at home.
Neurostimulators provide real-time therapeutic intervention.
Cognitive testing apps use AI algorithms to track brain performance over time.
These innovations are critical for early detection of brain disorders, especially in underserved or rural areas.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Brain Diagnostics
AI-powered software is being integrated into brain scan machines for rapid image interpretation, pattern recognition, and diagnostic prediction. Key benefits include:
Reduced diagnostic errors
Automated tumor detection
Personalized treatment plans
Real-time decision support for neurologists
Machine learning is rapidly becoming a pillar of next-generation neurology diagnostics.
Future Trends in Brain Diagnostic Technologies
Neuroimaging with higher spatial resolution
Hybrid imaging systems (PET-MRI)
AI-driven diagnostic algorithms
Integration with brain-computer interfaces (BCIs)
Non-invasive blood biomarkers for brain diseases
As these technologies evolve, BrainScript stays committed to exploring, explaining, and equipping clinicians and researchers with the latest in brain diagnostic innovation.
Conclusion
From MRI machines to portable EEG devices, modern brain diagnostic instruments have transformed how we approach neurological care. These tools not only enhance early detection but also open doors to personalized, data-driven treatments for complex brain disorders.
At BrainScript, we aim to bridge the gap between medical innovation and clinical application because a well-diagnosed brain is the first step toward better mental health and neurological resilience.